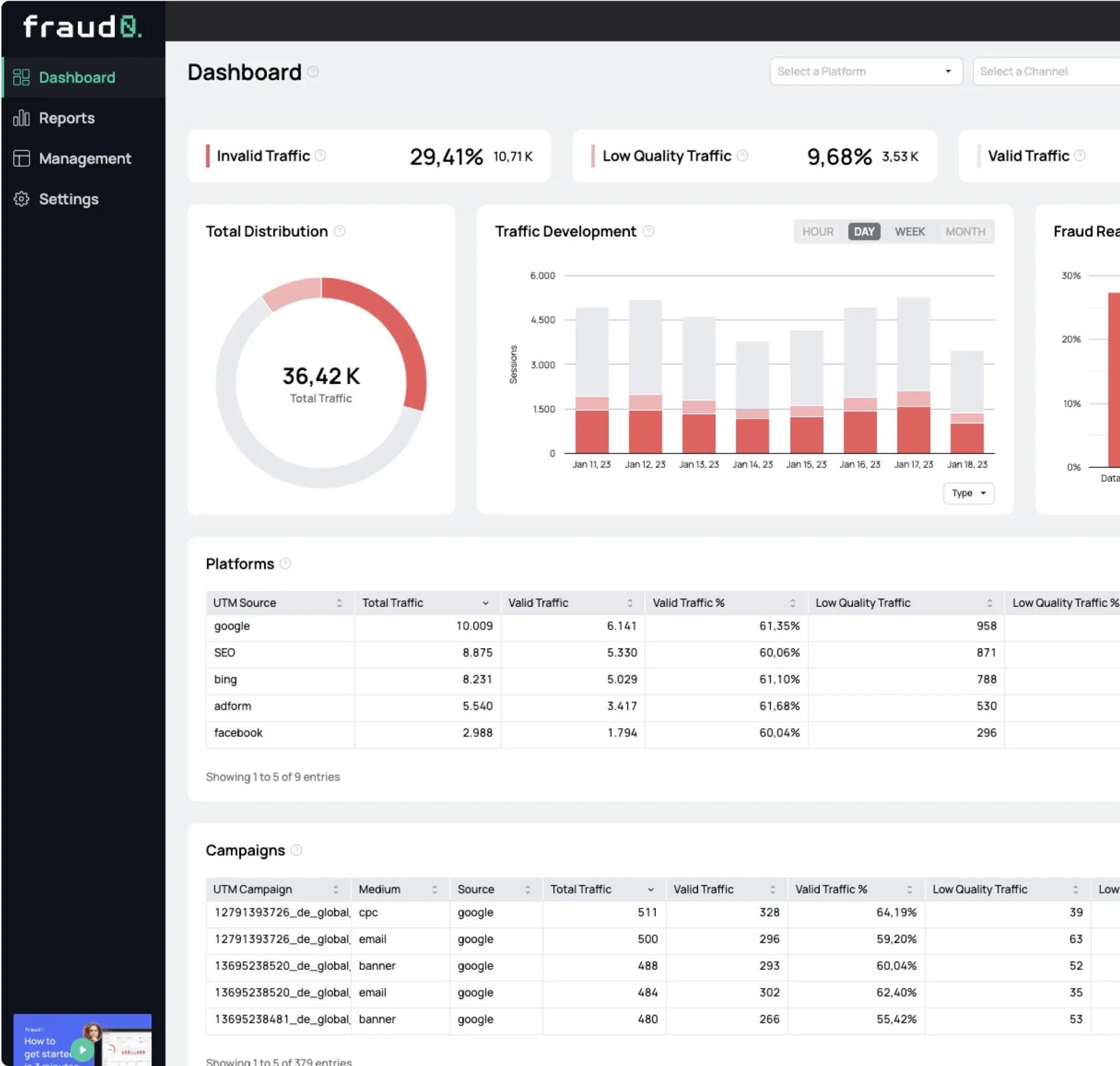
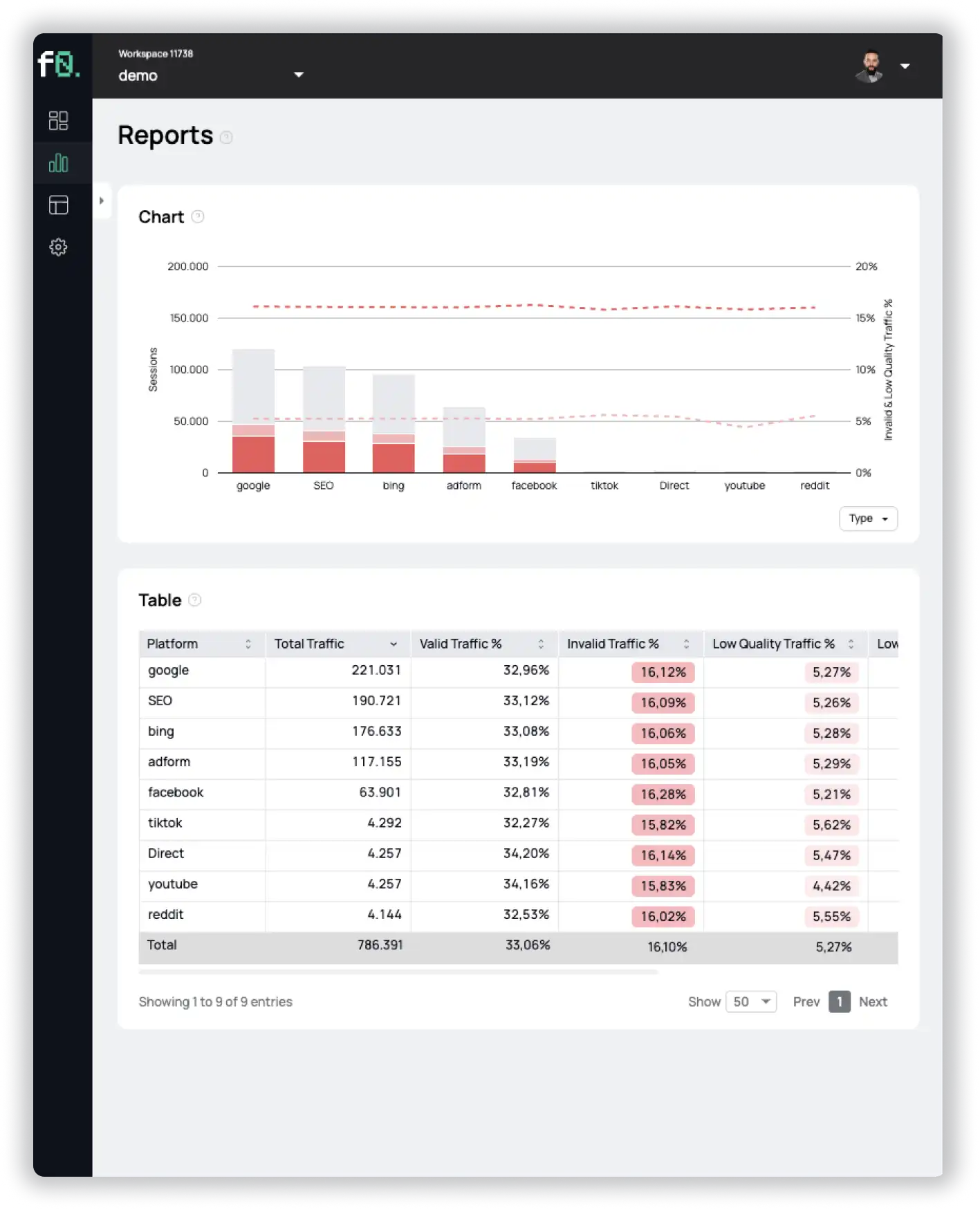
What is Retargeting Fraud and how to protect your ad budget
- Blog
Retargeting fraud is one of the most common types of ad and click fraud.
This article describes the process of retargeting fraud and gives tips on how to protect your advertising budget.
What is retargeting?
Retargeting is a digital marketing technique used to show ads to people who have previously interacted with a website or app. In most cases, it involves placing a cookie on the user’s browser and then displaying relevant ads to them across various platforms.
Suppose that you visited an e-commerce website, looked through the products, added an item to your cart, but left without making a purchase. Afterward, while you are browsing the internet, you will begin to see ads from that e-commerce site, encouraging you to reconsider and make a purchase.
Retargeting is an effective way to re-engage potential customers and increase conversions:
- Users, who are retargeted with display ads are 70% more likely to convert on the retailer’s website
- Retargeted customers are three times more likely to click on your ad than people who haven’t interacted with your business before.
- Retargeting cart abandoners can increase conversion rate up to 26%
The important thing to remember: Retargeting ads for a website are displayed only to users who have visited it in the past.
What is Retargeting Fraud?
So if ads are only shown to visitors who have already visited a website, how can retargeting fraud occur?
The answer is simple and in one word: bots. But to understand the big picture, we need to look at how bots work and how fraudsters make money with retargeting fraud.
Step 1 – Creating a fake website with plagiarized content
Fraudsters create fake websites with plagiarized content and register them with various advertising networks (e.g. Google Ads). This allows them to implement ads on their website and generate money from it. Nowadays, the creation of such fake websites can be done in a few seconds and is fully automated.
Step 2 – Use of sophisticated bots
The next step is to use the bots. These are programmed to behave like real people on a website. This includes faking technical characteristics such as the user agent string, the operating system, or the IP address, but also numerous on-site factors such as the navigation of the website, mouse movements, placing products in the shopping cart, and, above all, interacting with and accepting an existing cookie banner.
Many of these characteristics are randomized with each website visit. For example, the bot changes the IP address, time spent on the site, and product choices each time.
Step 3 – Search for high-quality keywords
In most cases, the fraudsters target high-value ad keywords, such as “life insurance”, “motorcycle accident lawyer” or “online business degree”. The bots’ goal is to select profitable ad keywords so that the fraudsters can increase their revenue.
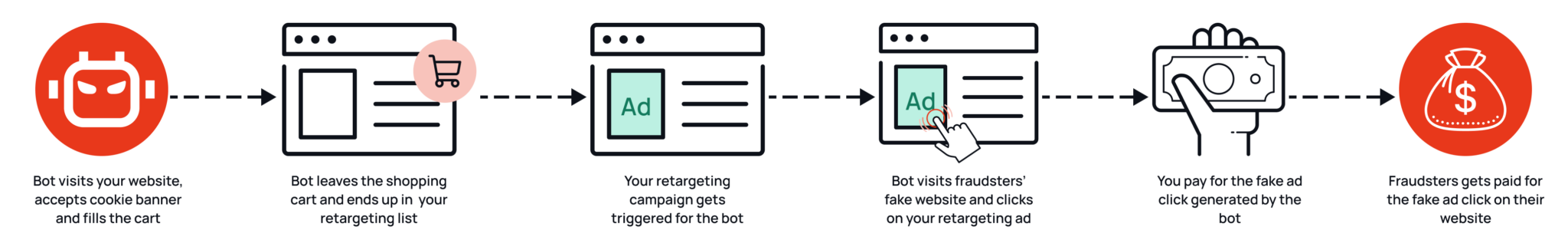
Step 4 – Bots visit websites to end up in retargeting lists
The bot searches for one of the keywords on a search engine like Google and visits the search results (both paid and organic). On the websites, it behaves like a real human: it visits various subpages, adds products to the shopping cart and fills in contact forms. In this step, the bot collects (retargeting) cookies from the websites it visits, as they mistake it for a real user.
Step 5 – Bots return home and the fraudster makes money
The bot then goes back to the fake website of the fraudster after visiting hundreds or even thousands of websites in this way. The banner ads of the websites it has previously visited are waiting for it there, as it has landed in countless retargeting lists by this point. It clicks on these banner ads and with every click the fraudster earns money.
Step 6 – Bots mimic human behavior to siphon off more money
In order not to be blocked by the ad networks, the bot can also perform some fake conversions on some advertisers’ websites in the last step. This is also known as Conversion Fraud. The goal is still to make the bot look like a real visitor and continue to benefit from the retargeting of the websites.
That, in a nutshell, is the process fraudsters use to make money with fake websites and the use of bots. The bot tricks the ad networks into displaying high-value retargeting ads on the fraudsters’ fake websites, which it then clicks on.
Taking into account the countless fraudsters with countless fake websites and who sometimes have thousands of bots in use at the same time, the estimated damage to the advertising industry totals 100 billion dollars per year.
How does Retargeting Fraud hurt your Marketing?
Retargeting Fraud impacts your marketing similar to general ad and click fraud in various ways:
- Waste of ad budget You pay for clicks on your retargeting ads. But instead of real people, bots visit your site.
- Skewed analytics data As a business, you need to rely on your data to make important decisions. Bots skew your analytics data, which can cause you to make entirely wrong decisions and waste your advertising budget even further on unwanted traffic.
We’ve written extensively about the impact of bots and invalid traffic on your marketing in the past on our blog. You can find more information on the topic in our article “The impact of invalid traffic on your marketing”.
How to protect yourself from Retargeting Fraud
The simplest way to protect the advertising budget from retargeting fraud is to avoid retargeting altogether. However, this would also mean that companies would lose the potential to win real customers.
Manual detection of bots and their exclusion from advertising channels, e.g., based on the IP address, is also not feasible. Bots can now mimic human behavior in great detail and change IP addresses with every website visit, making manual detection simply impossible.
The solution to this problem lies in the use of a bot detection and prevention software. fraud0 detects bots in real time and excludes them from retargeting by using Negative Audience Lists. This means that you no longer waste your advertising budget on bots, but can focus on real people who have a genuine interest in your product.
Sign up today for a free 7-day trial and see for yourself.
Retargeting Fraud FAQs
Retargeting fraud exploits advertisers who invest in retargeting campaigns that target people who have previously interacted with their website. The fraud is conducted by bots that are programmed to imitate human behavior – for example, by visiting a website or adding products to a cart. Thus, advertisers pay for ads to bring bots back to their website.
Retargeting Fraud impacts your marketing in various ways by wasting your ad budget, skewing your analytics data and hurting your overall brand.
The most effective way to prevent Retargeting Fraud is through bot detection software like fraud0, which identifies bots in real time and excludes them from your retargeting campaigns.
- Published: March 8, 2023
- Updated: July 2, 2025

See what’s hidden: from the quality of website traffic to the reality of ad placements. Insights drawn from billions of data points across our customer base in 2024.
1%, 4%, 36%?